Introduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a Java API to connect and execute the query with the database. It is a specific from Sun Microsystem that provide a standard abstraction(API or Protocol)
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) which defines how a client may access a database. JDBC is like a bridge between a Java application and a database.
for Java application to communicate with various databases. It provides the language with Java database connectivity standards, It is used to write programs required to access databases. JDBC, along with the database driver, can access databases and spreadsheets. The enterprise data stored in a relational database(RDB) can be accessed with the help of JDBC APIs.
Definition of JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
JDBC is an API(Application Programming interface) used in Java programing to interact with database. The classes and interface of JDBC allow the application to send requests made by users to the specified database.
Purpose of JDBC
Enterprise applications created using the JAVA EE technology need to interact with databases to store application-specific information. So, interacting with a database requires efficient database connectivity, which can be achieved by using the ODBC(Open database connectivity) driver. This driver is used with JDBC to interact or communicate with various kinds of databases such as Oracle, MS Access, Mysql, and SQL server database.
Components of JDBC
There are generally four main components of JDBC through which it can interact with a database. They are as mentioned below.
1. JDBC API: It provides various methods and interfaces for easy communication with the database. It provides two packages as follows, which contain the java SE and Java EE platroms to exhibits WORA (write once run anywhere) capabilities. The java.sql package contains interface and classes of JDBC API.
java.sql: This package provides APIs for data access and data process in a relational database, included in Java Standard, included in Java Standard Edition (java SE)
javax.sql: This package extends the functionality of java package by providing datasource interface for establishing connection pooling, statement pooling with a data souce, included in Java Enterprise Edition (java EE)
It also provides a standard to connect a database to a client application.
2. JDBC Driver Manager: It load a database-specific driver in an application to establish a connection with a database. It is used to make a database-specific call to the database to process the user request.
3. JDBC Test Suits: It is used to test the operation(such as insertion, deletion, updation) being performed by JDBC Drivers.
4. JDBC-ODBC Bridge Drivers: It connects database drivers to the database. This bridge translates the JDBC method call to the ODBC function call. It makes use of the sun.jdbc.odbc package which includes a native library to access ODBC characteristics.
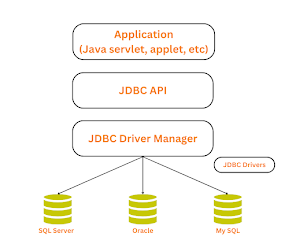 |
| Architecture of JDBC |
Description:
1. Application: It is a java applet or a servlet that communicates with a data source.
2. The JDBC API: The JDBC API allows Java program to execute SQL statements and retrieve results. Some of the important classes and interfaces defined in JDBC API are as follows:
3. Driver Manager: It plays an important role in the JDBC architecture. It uses some dtabase-specific drivers to effectively connect enterprises application to databases.
4. JDBC Driver: To communicate with a data source through JDBC, you need a JDBC driver that intelligently communicates with the respective data source.
What is API?
Before jumping into JDBC Drivers, let us know more about API.
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It is essentially a set of rules and protocols which transfers data between different software applications and allow different software applications to communicate with each other. Through an API one application can request information or perform a function from another application without having direct access to it’s underlying code or the application data.
JDBC API uses JDBC Drivers to connect with the database.
JDBC Drivers
JDBC drivers are client-side adapters (installed on the client machine, not on the server) that convert requests from Java programs to a protocol that the DBMS can understand. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers;
1. Type-1 driver or JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
2. Type-2 driver or Native-API driver (partially java driver)
3. Type-3 driver or Network Protocol Driver (fully java driver)
4. Type-4 driver or Thin driver (fully java driver)
Interfaces of JDBC API
A list of popular interfaces of JDBC API is given below:
- Driver interface
- Connection interface
- Statement interface
- PreparedStatement interface
- CallableStatement interface
- ResultSet interface
- ResultSetMetaData interface
- DatabaseMetaData interface
- RowSet interface
- DriverManager class
- Blob class
- Clob class
- Types class
The above example demonstrates the basic steps to access a database using JDBC. The application uses the JDBC-ODBC bridge driver to connect to the database. You must import java.sql package to provide basic SQL functionality and use the classes of the package.
What is need of JDBC?
JDBC is a Java database API used for making connection between java applications with various databases. Basically, JDBC used for establishing stable database connection with the application API. To execute and process relational database queries (SQL or Oracle queries), multiple application can connect to different types of databases which supports both standard (SE) and enterprise (EE) edition of java.





Comments
Post a Comment